
The tertiary structure can therefore be deranged if there is disruption to the bonds between R groups, causing the structure to lose its shape and resulting in a loss of function. Folding of the polypeptide chain occurs via an i nteraction between the R groups of amino acids. This tends to be globular in shape and contains a binding site for the protein action. Tertiary protein structure is the folding of the polypeptide chain into a unique 3D structure. The sheets can be in parallel or antiparallel.īy Thomas Shafee, via Wikimedia Commonsįig 3 – Structure of an alpha helix and beta-pleated sheet Tertiary Protein Structure Beta-pleated sheet – formed by hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl group of one amino acid on one sheet and the hydrogen molecule of an amino acid on another sheet.The strong bonds and stability of this structure give it a strong tensile strength, which allows it to form the shape seen in DNA. Alpha-helix – a coil formed by hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl group and the amino group of different amino acids.Secondary protein structure is the repetitive folding of polypeptide chains by hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl (OH) group and the hydrogen molecule of the adjacent amino acid, leading to the unique shape of the protein. The most common examples are the alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheets. These bonds form between the N terminal and C terminal of amino acids and are highly resistant to heat or chemicals.Īny mutation in this amino acid sequence can affect protein folding, leading to problems with the protein’s function. Primary protein structure is when amino acids bound are together via covalent peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. Athletes commonly know that Valine is vital for the muscle metabolism and the growth of muscle tissue as it assists in maintaining the proper amount of nitrogen in the body.By Kep17, via Wikimedia Commonsįig 2 – Overview of protein structure. Besides, this amino acid helps them recover tissues damaged during physical activity. This amino acid also greatly improves the regulation of the immune system, but probably the greatest benefits of Valine are experienced by athletes performing long-distance sports and bodybuilding, because this amino acid is important for the muscle tissue recovery and for the muscle metabolism, while increasing exercise endurance.īodybuilders usually use Valine together with Isoleucine and Leucine to promote muscle growth and to supply them with an energy. Besides, it is also proved to help alleviate disorders of the muscles, and to be an effective appetite suppressant. Valine provides numerous benefits like improvement in insomnia and nervousness. You can obtain it through kidney beans, leafy vegetables, poultry and milk. This particular amino acid is not processed by the liver, but is taken up by muscles. Valine is important for everyday body functions and for maintaining muscles, as well as for the regulation of the immune system. This amino acid cannot be produced by your body and must be obtained through food or through supplements. Valine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids, along with Leucine and Isoleucine. In other words, Valine is an essential amino acid important for smooth nervous system and cognitive functioning. Valine is also a precursor in the penicillin biosynthetic pathway and is known for inhibiting the transport of Tryptophan across the blood-brain barrier. This amino acid aids preventing the breakdown of muscle, because it supplies the muscles with an extra glucose responsible for the energy production during physical activity. Other names: L-2-Amino-3-methylbutyric acid (S)-α-Aminoisovaleric acid L-alpha-Aminoisovaleric acid
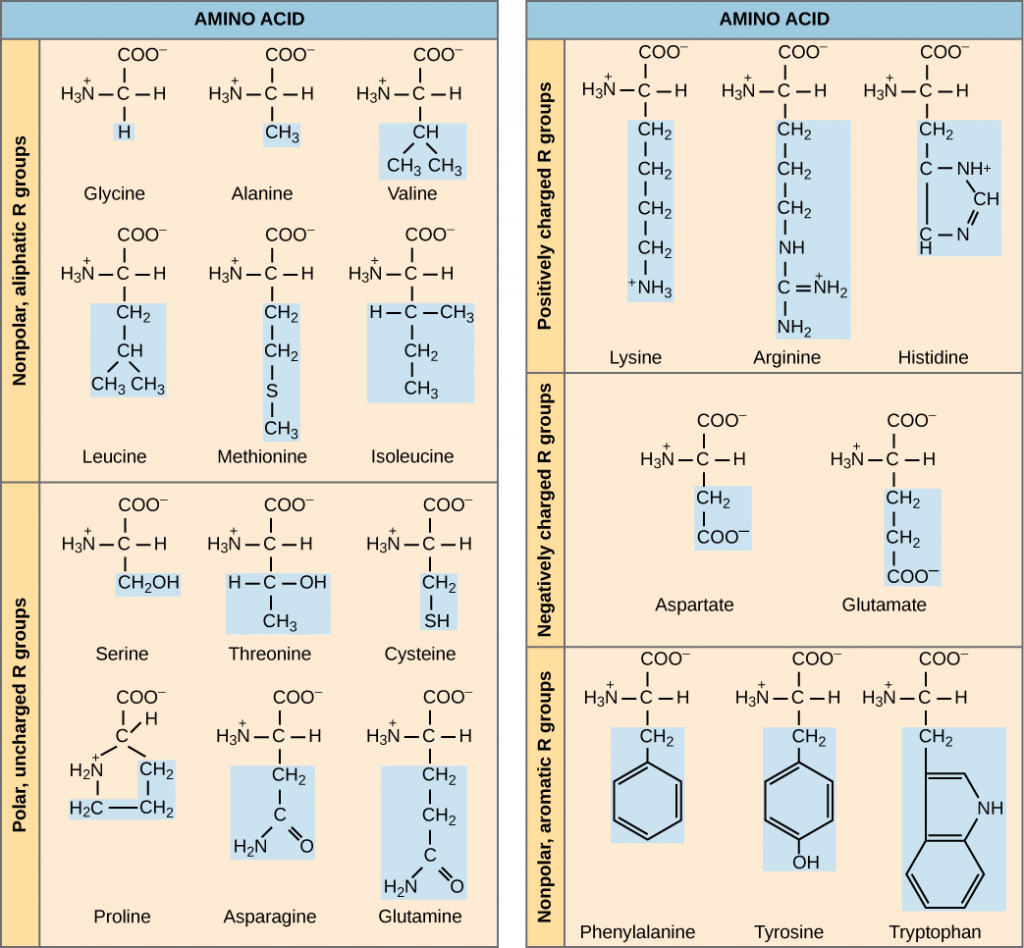
Isomeric SMILES: Identifier: RVEPXRXYSLTFTD-UHFFFAOYAI Molecular Formula (Structural Formula): C5H11NO2 Molecular Weight (Molar Mass): 117.14634 g/mol IUPAC Name: (2S)-2-Amino-3-methylbutanoic acid Chemical structure of L-Valine Identifiers and properties of Valine Actually, three branched-chain amino acids constitute over 2/3 of the amino acids in the body proteins, pointing out that its role for humans is invaluable. Today Valine is recognized as the branched-chain essential amino acid providing a stimulant activity. Emil Fischer has isolated Valine from casein back in 1901, which was achieved by hydrolyzing proteins.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
